What is Q and the Problem of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) Governance
Posted on July 28, 2024 by Admin
What is DAO?
A DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is a decentralized entity that operates based on rules encoded as smart contracts on the blockchain. A DAO lacks a centralized management structure, with decisions made through the consensus of its community members, typically via token-based voting.
The Problem of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) Governance
Traditional DAOs face several challenges, including:
- Slow Decision-Making Processes: Achieving consensus from a large and diverse group of members can be time-consuming, particularly in urgent situations.
- Lack of Clear Governance Structures: Many DAOs lack well-defined governance frameworks, leading to potential power abuse and inefficient decision-making.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts in DAOs can have security loopholes, making them susceptible to attacks and exploits.
- Difficulties in Dispute Resolution: Traditional DAOs often lack robust mechanisms for resolving disputes, resulting in prolonged conflicts and unresolved issues.
- Legal Risks: Operating in a legally ambiguous environment, DAOs face significant regulatory and legal challenges.
- Member Participation Issues: Ensuring active and equitable participation from all members can be difficult, with some members being more engaged than others.
What is Q?
Q is a decentralized governance layer designed for Web3, introducing the concept of Shared Governance Security. It serves as a foundational component in the modular blockchain stack, enabling secure and efficient governance for various protocols and applications. Q aims to provide an instant security upgrade and address some of the most pressing issues in the crypto space, such as preventing governance exploits and reducing legal and regulatory risks associated with centralized decision-making. Additionally, Q expands the possibilities on-chain, facilitating innovative business models in Web3.
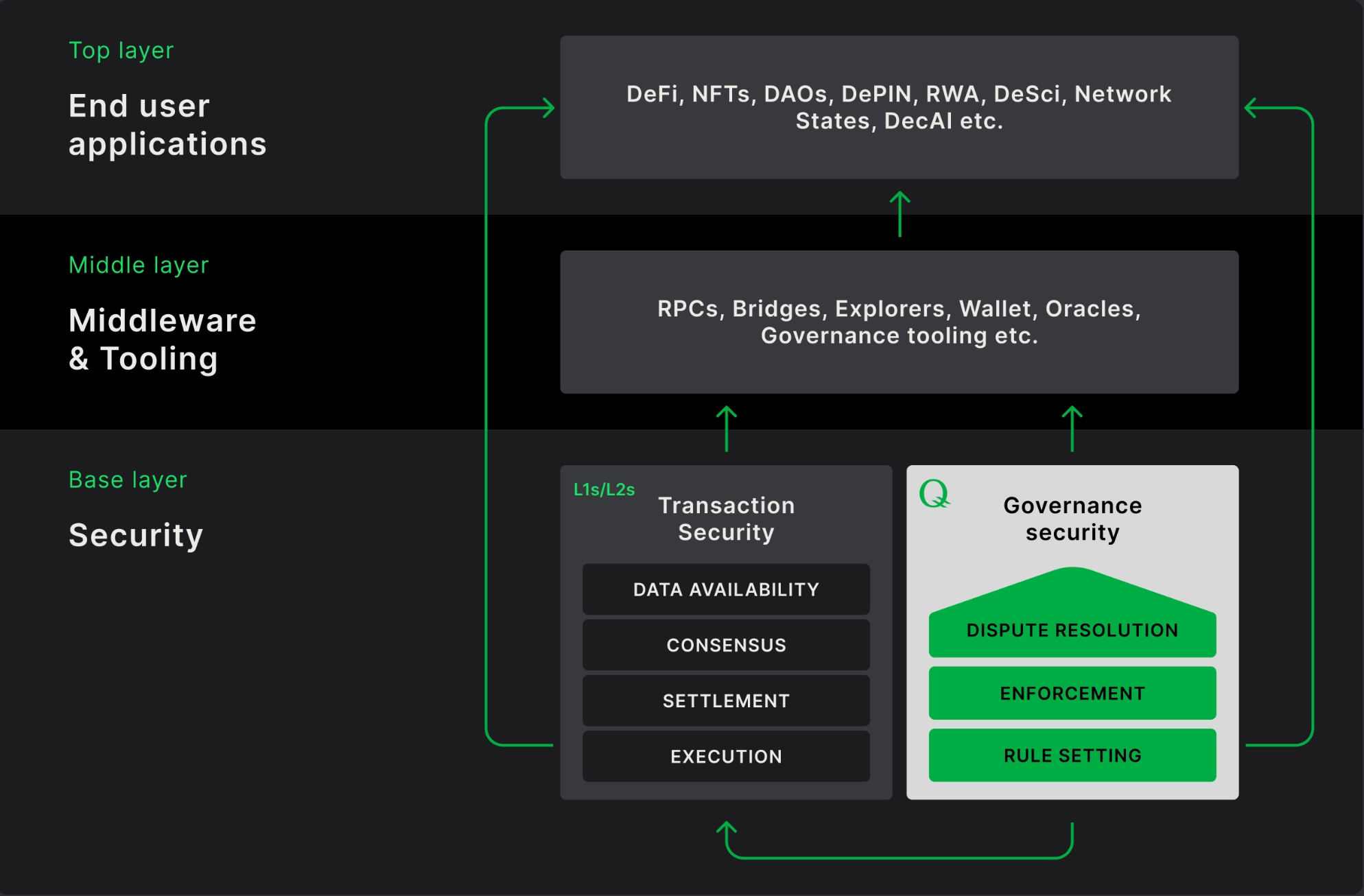
Q impacts all layers of the blockchain ecosystem, from the base layer to the end-user application layer. Here is a comprehensive overview of how Q influences each layer:
1. Base Layer: Security
Transaction Security: Q provides security mechanisms to ensure the integrity and security of transactions on the blockchain. This includes ensuring data availability, achieving consensus, settling transactions, and executing transactions.
2. Middle Layer: Middleware & Tooling
Middleware & Tooling: Q offers the necessary infrastructure for decentralized applications, including tools such as RPCs, bridges, blockchain explorers, wallets, oracles, and governance tooling. These tools facilitate connection and interaction between different components of the ecosystem.
3. Top Layer: End User Applications
End User Applications: Q supports a variety of decentralized applications, including Decentralized Finance (DeFi), NFTs, DAOs, DePIN, Real World Assets (RWA), Decentralized Science (DeSci), and Decentralized AI applications. These applications provide services and functionality directly to end-users.
The Issues that the Q System is Addressing:
- Slow Decision-Making Processes: Uses a clear governance structure with three core elements: rule-setting, enforcement, and dispute resolution. This system employs smart contracts and voting mechanisms to speed up the decision-making process, making it faster and more efficient
- Lack of Clear Governance Structures: Provides a clear and comprehensive governance structure with checks and balances through Root Nodes and Validator Nodes, ensuring transparency and fairness in the decision-making process
- Security Vulnerabilities: Offers a shared governance security layer and private arbitration mechanisms to protect the system from attacks and security breaches, enhancing the overall security of the ecosystem..
- Difficulties in Dispute Resolution: Uses Root Nodes and private arbitration mechanisms to resolve disputes fairly and transparently, ensuring issues are handled effectively.
- Legal Risks: While it cannot completely eliminate legal risks, Q mitigates these risks by providing a shared and decentralized governance mechanism, ensuring decisions are made transparently and more legally compliant.
- Member Participation Issues: Encourages community participation through clear voting and election systems, enhancing democracy and member involvement in the decision-making process.
How does it work?
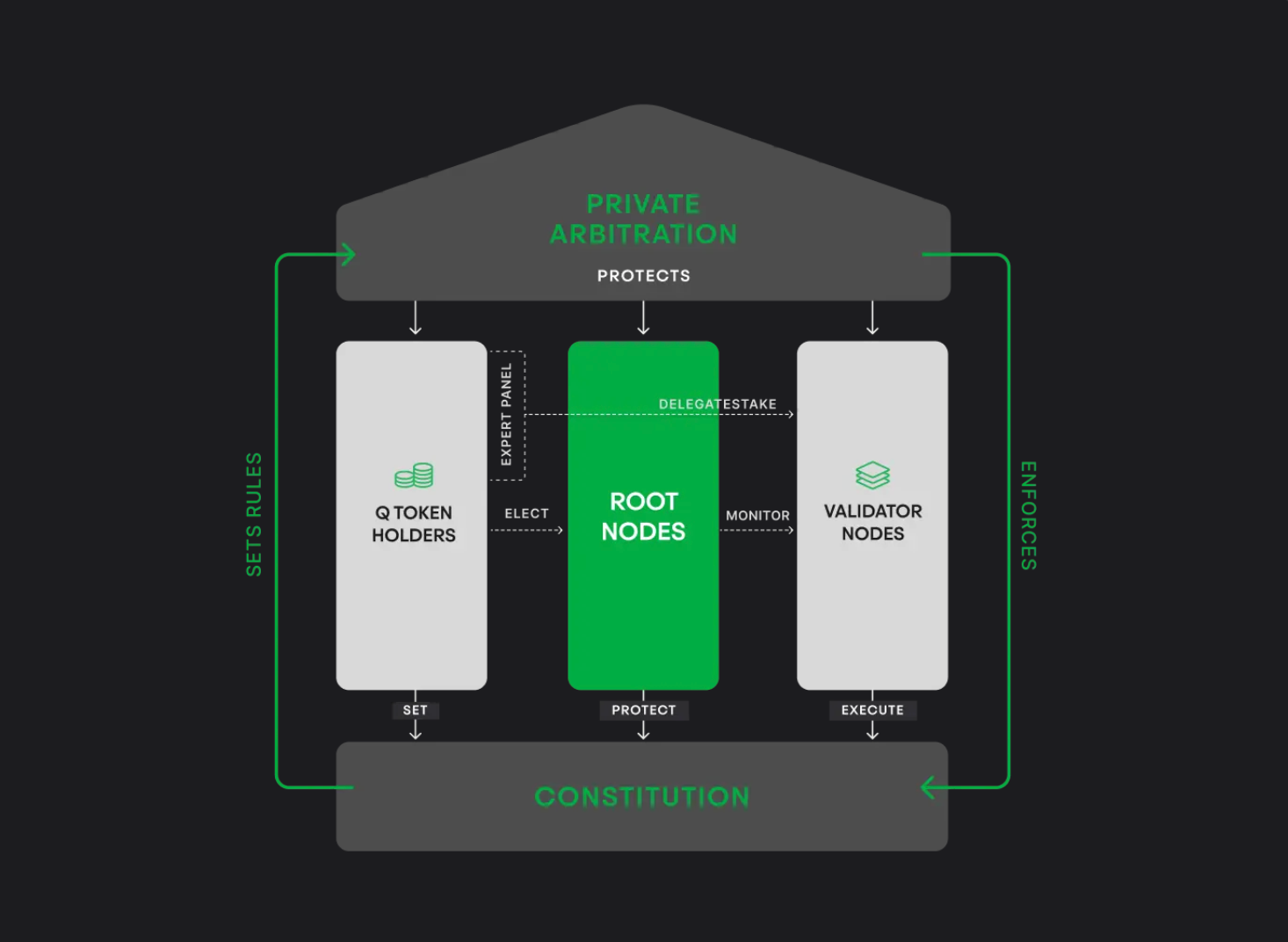
Q uses a decentralized governance structure based on three main elements: rule setting, enforcement, and dispute resolution.
- Rule Setting: Q Token Holders, Elect an expert panel to establish governance rules.
- Enforcement: Validator Nodes, Ensure transactions comply with established rules.
- Dispute Resolution: Root Nodes: Monitor validators and resolve disputes through private arbitration.
Protection and Integrity
Private Arbitration: Protects the system from disputes and ensures integrity.
Q is a core piece of the modular blockchain stack, designed to protect real value and ensure transparency, security, and fairness.
Explore Q Ecosystem
1. Q Tokens (QGOV)
- Q Tokens (QGOV): These are the native assets of the Q blockchain. Validators and root nodes must stake QGOV in dedicated smart contracts on the Q blockchain to ensure the network's security.
- Value is not fixed: The value of QGOV is not fixed or pegged to any specific price but is determined by supply and demand in the market.
- Benefits for holders: QGOV holders benefit from using the system through transaction fees and other fees generated within the Q system.
2. Q Token Holders
- Ownership and governance participation: QGOV holders have the right to directly participate in the governance decisions of Q. They can delegate or allocate all or part of their tokens to validators or candidates, thereby increasing the amount of QGOV staked for these positions.
- Pseudonymous Ownership: Ownership of QGOV is pseudonymous, with no need to disclose one's identity.
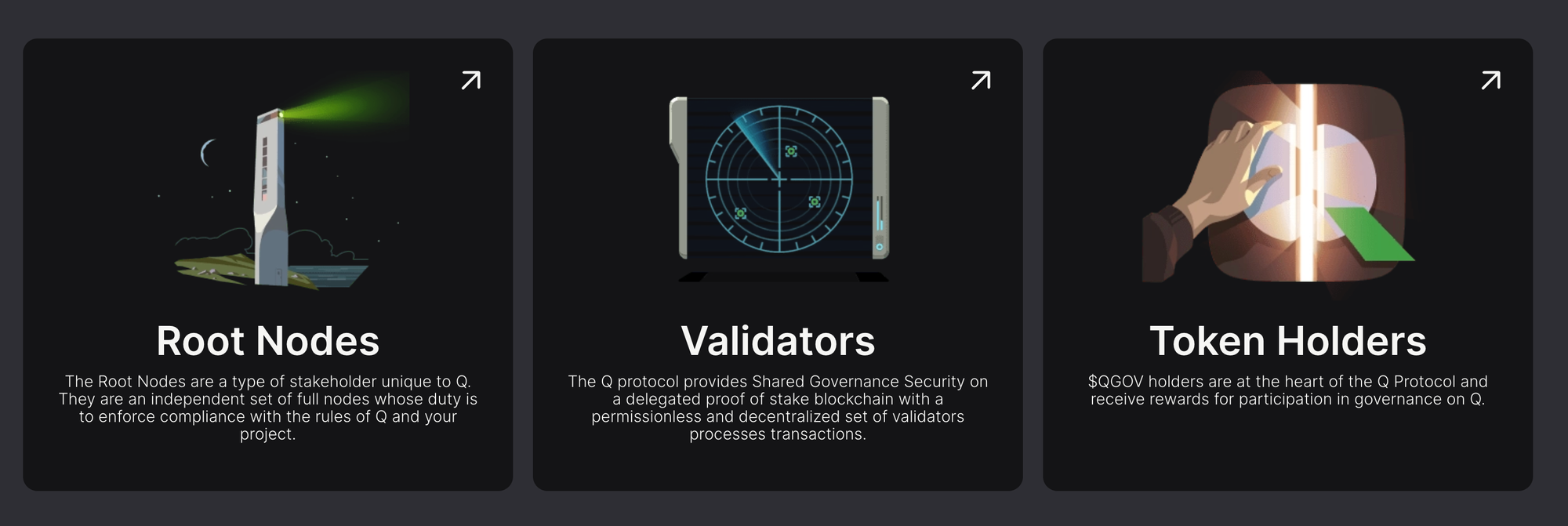
3. Validators and Root Nodes
- Validators: Maintain and secure the Q blockchain by validating transactions, forming blocks, and recording valid transactions. They must run up-to-date software and operate a full Q node at all times.
- Root Nodes: Monitor validators to ensure compliance with the Q constitution. Root nodes do not validate transactions but ensure security and oversight of the validators' actions.
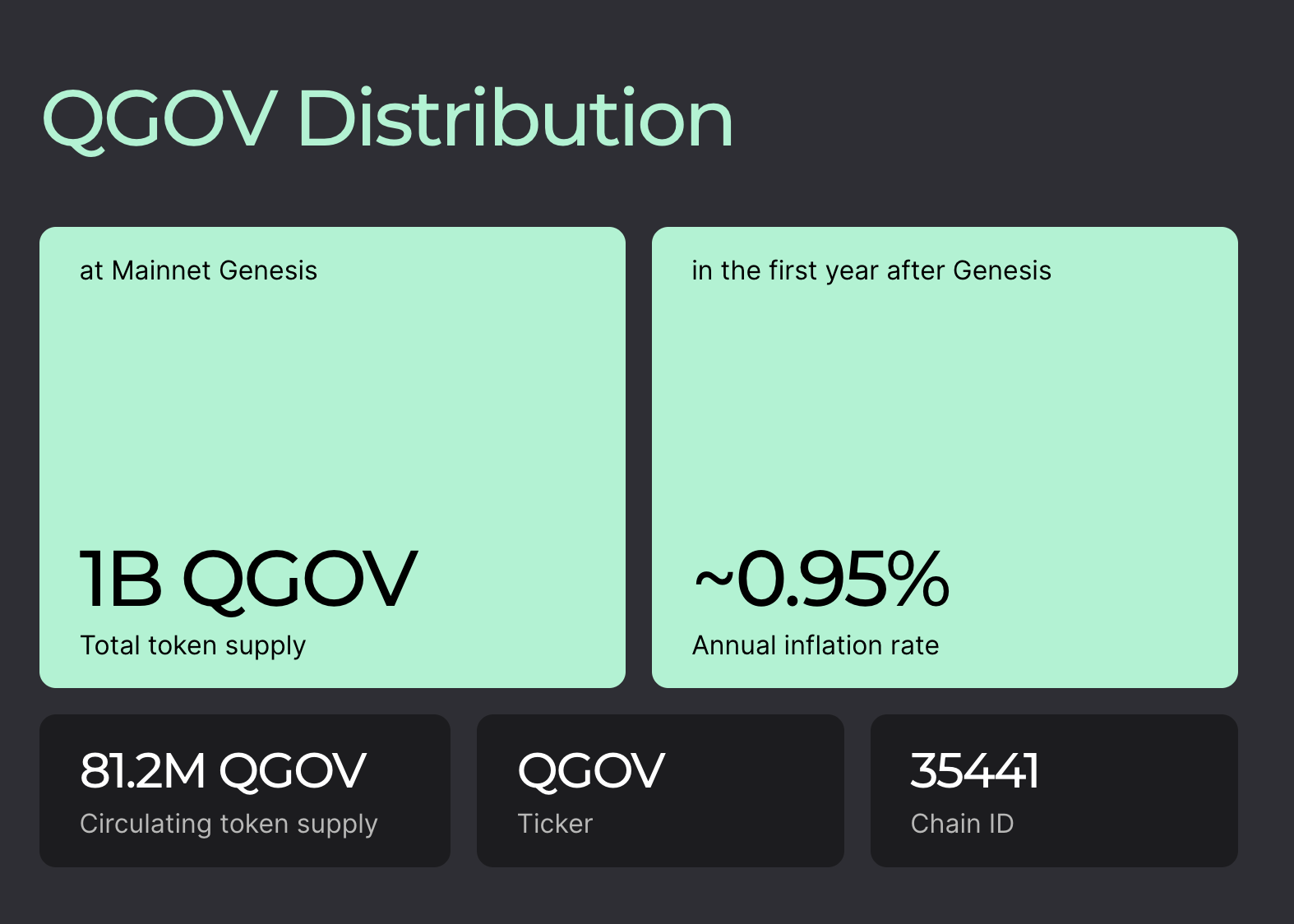
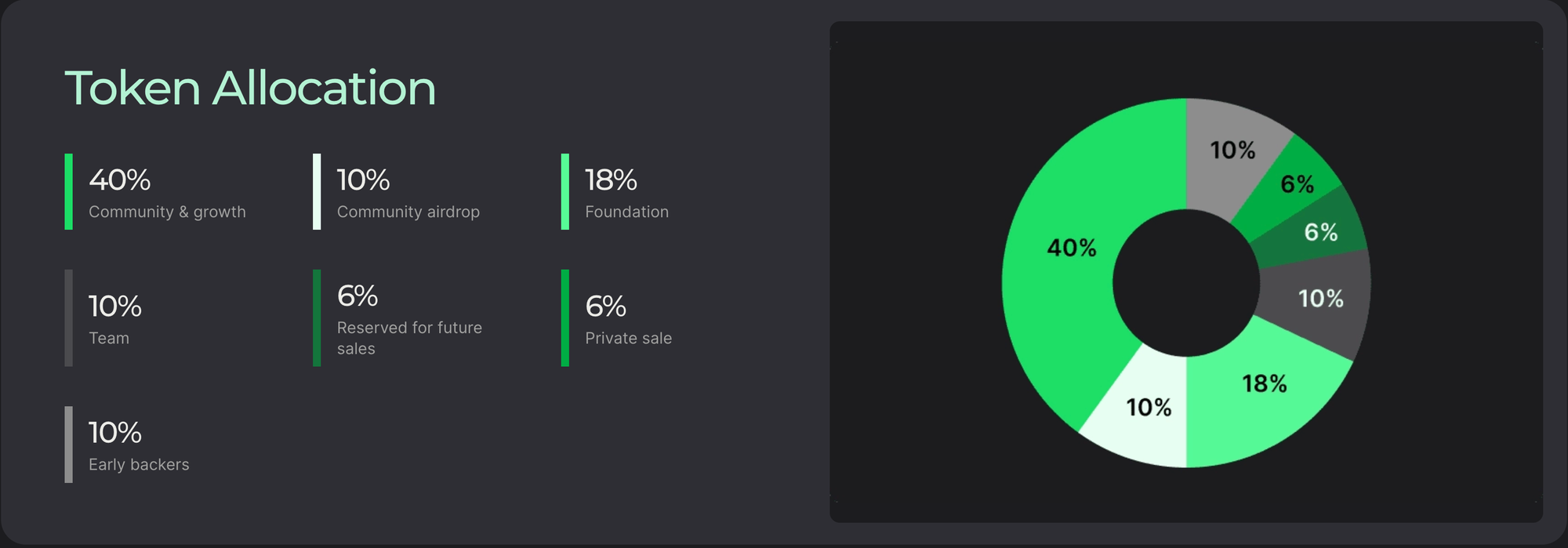
- Low inflation rate: The annual inflation rate of approximately 0.95% is quite low, helping to maintain the value of the token over time and avoiding high inflation.
- Community and growth: Allocating 40% of the tokens for community and growth shows a focus on developing the ecosystem and encouraging community participation.
Who are Q Backers and Investors?


HashKey Capital:
- Acts as an early investor and participates in the governance of Q by operating a Root Node.
- Contributes to the security and stability of the Q network.
Greenfield One:
- The lead investor in the first private sale, supporting the launch of Q’s mainnet.
- Operates both a Validator and a Root Node on the testnet and mainnet, enhancing the resilience and reliability of Q’s networks.
The collaboration between Q, HashKey Capital, and Greenfield One not only provides financial support but also enhances the security and development capabilities of the Q ecosystem. The active participation of these investors in operating network nodes and participating in governance ensures the system's stability and transparency.
Use Cases of Q
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Lending and Borrowing: Secure and transparent platforms for lending and borrowing assets.
- Synthetic Assets: Financial applications like stablecoins and derivatives backed by collateral.
2. Governance and Voting Systems
- DAO Management: Robust framework for fair and transparent decision-making.
- Community Voting: Facilitates voting on proposals and important decisions in decentralized projects.
3. Dispute Resolution
- Private Arbitration: Mechanisms for resolving disputes in a decentralized, transparent manner.
4. Identity Verification
- Q ID: Identifies individuals for interactions requiring unique identification, useful for KYC processes and governance activities.
5. Tokenized Assets
- Asset Management: Facilitates creation and management of tokenized assets, allowing fractional ownership and trading of assets on the blockchain.
6. Supply Chain Management
- Transparency and Traceability: Ensures transparency and traceability of goods and services from production to delivery.
7. Gaming and NFTs
- In-Game Economies: Manages in-game economies with decentralized governance.
- NFT Marketplaces: Supports NFT creation, trading, and governance for digital collectibles.
8. Real Estate
- Property Tokenization: Allows for fractional ownership and easier transfer of property rights.
- Governance of Property: Manages governance of real estate projects for transparent decision-making.
Top post

Blockcast: Accelerating the Internet, Connecting the World
What is Blockcast? Blockcast is a next-generation Content Delivery Network (CDN) that uses multicast technology to address bandwidth challenges in the era of booming streaming. Born at UC Berkeley, the project aims to build a decentralized network that leverages community power to deliver high-quality content like 4K and 8K globally while slashing costs for providers. With the slogan "Content Delivery, Powered By You!", Blockcast is not just a technology but an ecosystem where anyone can parti
June 2, 2025

Analysis of Nockchain: A ZK-Proof-of-Work Blockchain
Introduction to Nockchain In the fast-evolving world of blockchain, Nockchain emerges as a unique project aiming to revolutionize decentralized computing. Founded in 2023 in Berlin, Germany, Nockchain is a high-throughput blockchain leveraging a Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machine (ZKVM) and a novel ZK-Proof-of-Work (ZKPoW) consensus mechanism. With its native token, $NOCK, and a promise of a fair launch, Nockchain has sparked interest in the Web3 community. However, controversies at its mainnet lau
May 29, 2025

Monad: The Future of Layer 1 Blockchain with Unparalleled Performance
As the blockchain industry continues to evolve, Monad emerges as a promising Layer 1 (L1) blockchain, delivering exceptional performance and scalability. Aiming for 10,000 transactions per second (TPS), a block time of just 0.5 seconds, and full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), Monad is capturing the attention of developers and users alike. Let’s dive into the details of this groundbreaking project and discover how you can get involved today! What is Monad? Monad is a La
May 12, 2025

Drosera Network: Revolutionizing DeFi Security and How to Run a Node
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has transformed the financial landscape, but with great innovation comes great risk. Since 2014, DeFi protocols have lost nearly $80 billion to exploits, highlighting the urgent need for robust security solutions. Enter Drosera Network, a decentralized security protocol built on Ethereum that aims to safeguard DeFi ecosystems through automated threat detection and response. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what Drosera Network is, why it matters, and provide a s
April 20, 2025

Gensyn: Revolutionizing AI Compute and Guide to Running a Node
Introduction to the Gensyn Project Gensyn is a decentralized Machine Learning Compute Protocol designed to connect global computing resources into a supercluster tailored for artificial intelligence (AI). Developed by a UK-based team, Gensyn aims to reduce the costs of training AI models, increase accessibility for researchers, engineers, and academics, and ensure transparency and censorship resistance through blockchain technology. Goals and Vision * Cost Reduction: Gensyn claims it can cu
April 14, 2025

Pipe Network: The Future of Decentralized CDN and Opportunities from the Node DevNet 2 Program
In the digital era, where the speed of content delivery is a critical factor, content delivery networks (CDNs) have become indispensable in ensuring a seamless user experience. However, giants like Cloudflare and Akamai, while powerful, remain constrained by their traditional centralized models. Enter Pipe Network—a decentralized CDN built on the Solana blockchain—emerging as a fresh contender promising to revolutionize how we approach content distribution. Notably, its current Node DevNet 2 pro
March 18, 2025