Dill and the Heavyweight Technologies Behind It
Posted on August 9, 2024 by Admin

What is Data Availability and What Are Its Limitations?
Data Availability is a crucial concept in blockchain technology, relating to ensuring that all the data necessary to verify and validate transactions or states within the blockchain is available and accessible to all nodes in the network. This is a key factor in maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain system, especially in systems that utilize sharding or other scalability solutions
Limitations of Data Availability:
- Data Availability Verification: One of the biggest challenges is how to ensure data availability without having to download and verify the entire data, which can be very resource-intensive. Methods like Data Availability Sampling (DAS) attempt to address this, but there is still a risk that small samples may not be representative of the entire data.
- Scalability:As the network expands with more transactions, ensuring data availability on a large scale becomes challenging. Scalability remains an issue, especially when trying to maintain high performance and security without increasing costs or complexity.
- Cost and Resources: Ensuring data availability requires significant resources, including storage capacity, bandwidth, and computational power. This can increase the operational costs of the network, especially when dealing with large volumes of data.
- Distribution and Decentralization: Another issue is how to ensure that data is evenly distributed across the network without relying on a few centralized entities. This is essential to maintain the decentralization of the network, but it is difficult to achieve.
- Security and Fraud Prevention: In cases where data is unavailable, nodes may be unable to verify the validity of blocks, leading to potential fraud. Defending against attacks and ensuring that no data is missing is a major challenge for the security of the system.
Dill and Which limitations has Dill addressed?
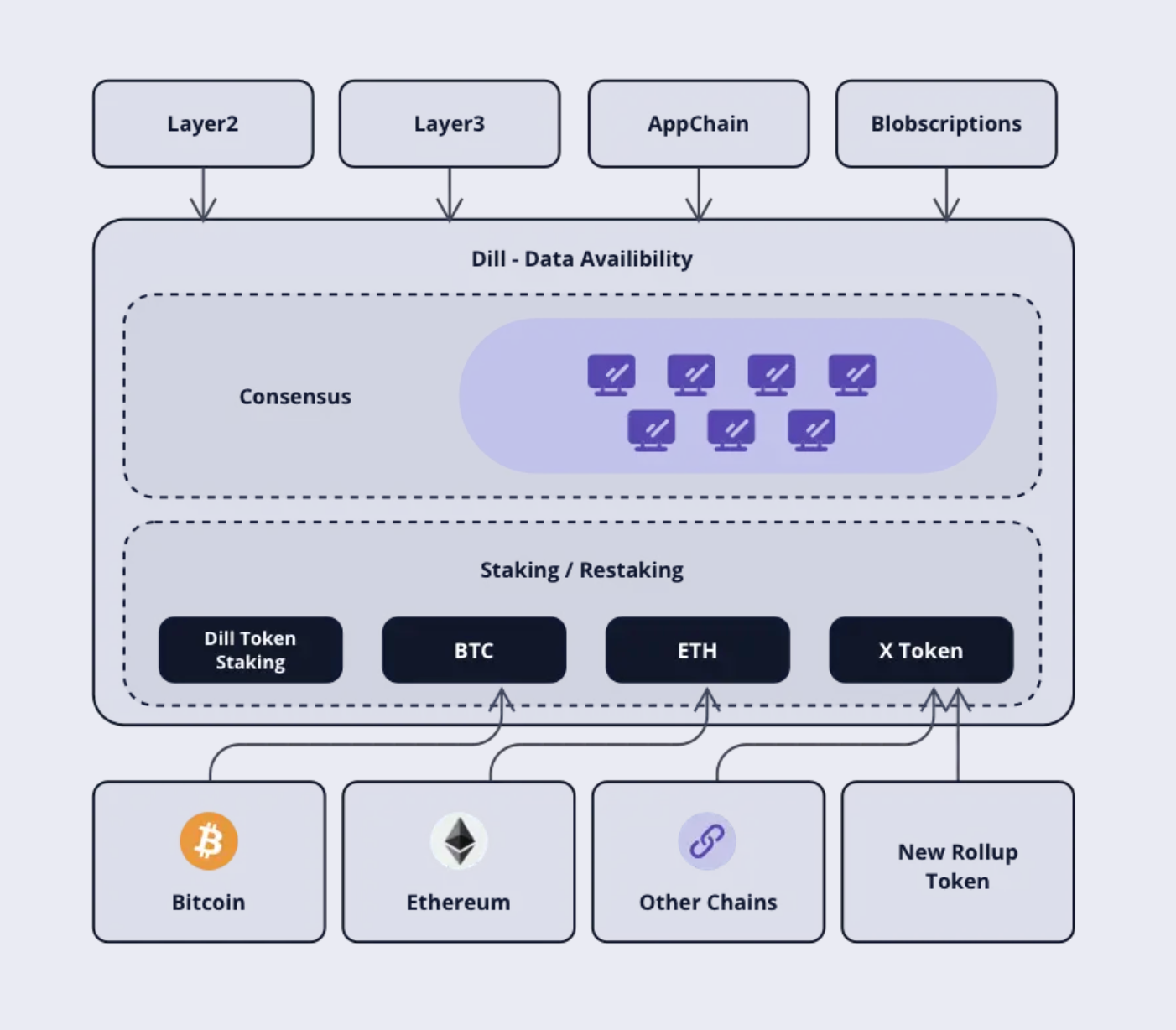
Dill is a high-scalable and highly secure next-generation DA (Data Availability) network. Dill aligns with the Full Danksharding technical solution in Ethereum's future roadmap, adopting core technologies such as subnet sharding, 2D EC (Erasure Coding), KZG (Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg), and DAS (Data Availability Sampling). It provides scalability that is 10 to 100 times greater than other current DA networks.
Dill has addressed several limitations of Data Availability through advanced technologies and optimized methods. Here’s how Dill has tackled some key issues:
- Data Availability Verification (Data Availability Sampling - DAS): Dill uses 2D Data Availability Sampling (DAS) technology, which allows for more efficient and reliable data sampling compared to traditional DAS methods. This ensures that data remains available and can be verified without needing to download the entire dataset.
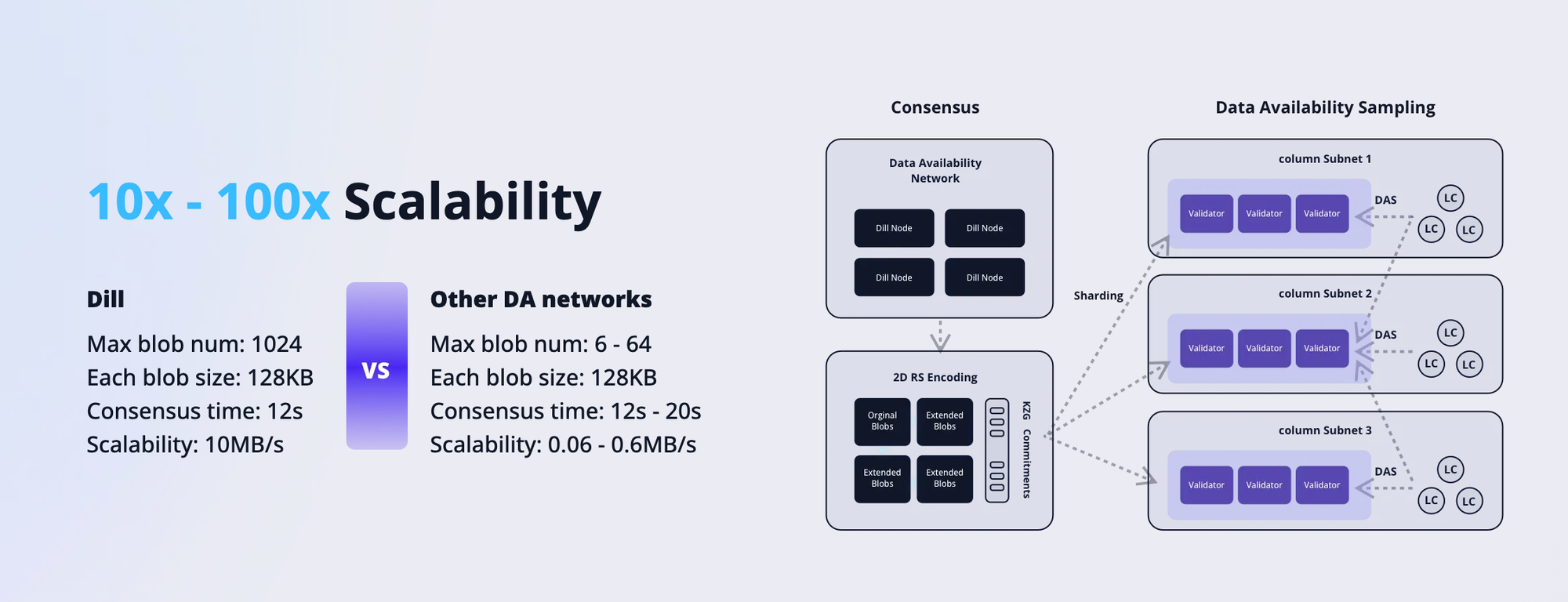
- Scalability: Dill significantly improves the scalability of the network by utilizing sharding and Reed-Solomon encoding (RS Encoding) combined with KZG Commitments. This allows Dill to process much larger amounts of data at a much faster rate, up to 10 to 100 times faster than other DA networks.
- Cost and Resources: By optimizing data storage and processing through technologies like erasure coding and Distributed Hash Table (DHT), Dill helps reduce costs and resource requirements while maintaining high performance.
- Distribution and Decentralization: Dill’s system ensures effective data distribution using DHT, helping to avoid centralization and reduce dependency on intermediary entities.
- Security and Fraud Prevention: With the implementation of KZG Commitments and other advanced security mechanisms, Dill enhances security during data availability verification, minimizing the risk of fraud and ensuring data is always verified safely.
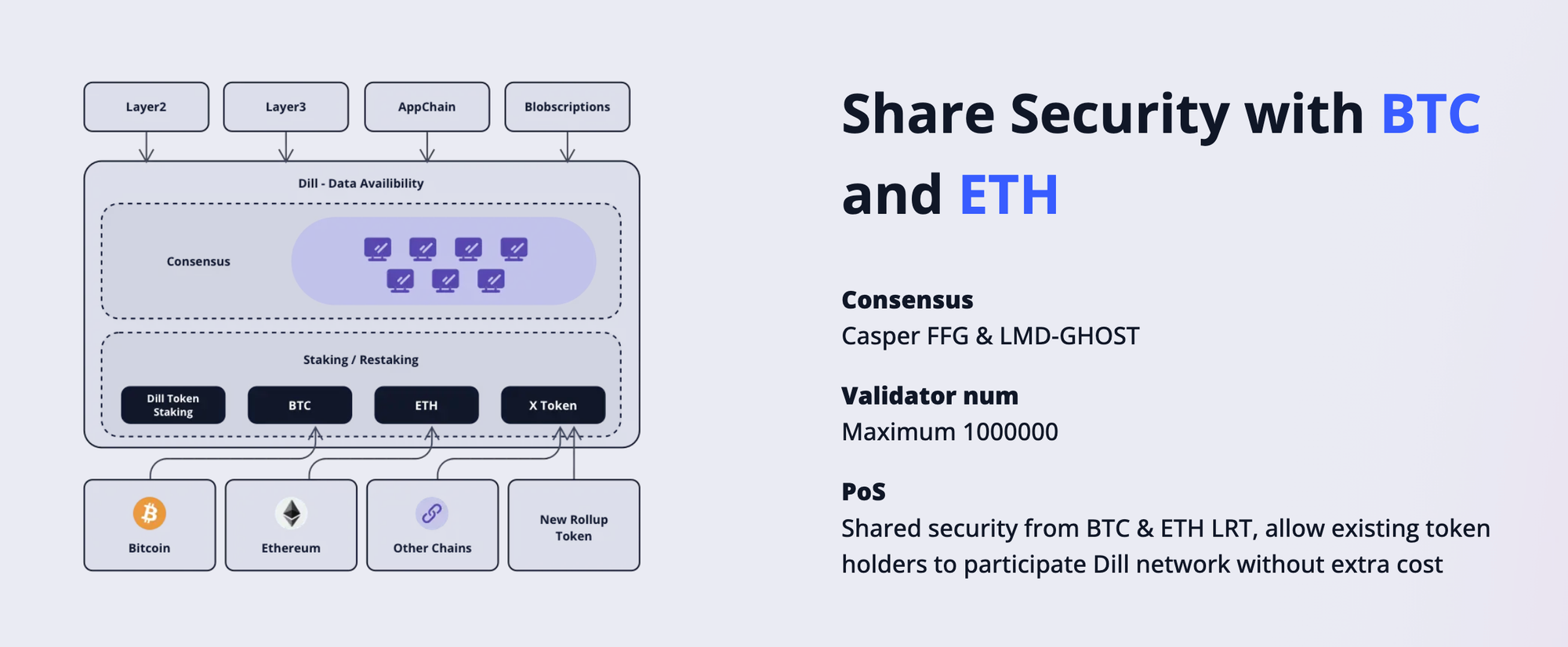
Additionally, Dill has the following strengths:
- Shared Security with BTC and ETH: Dill leverages the robust security infrastructure of Bitcoin and Ethereum, allowing users to use existing tokens on BTC and ETH to participate in the Dill network without incurring additional costs. This means that Dill not only relies on its own security but also combines and extends security from other large and reliable blockchain networks.
- Consensus Mechanism: Dill uses the Casper FFG and LMD-GHOST consensus mechanisms, both of which are improvements proposed for Ethereum 2.0, enhancing the security and efficiency of the consensus process. Casper FFG is a hybrid Proof of Stake (PoS) protocol, combining PoS and Proof of Work (PoW) to ensure security and scalability. LMD-GHOST is an optimized algorithm that helps consensus nodes select blocks to add to the chain based on specific rules, increasing the speed and accuracy of consensus.
- Number of Validators: The Dill network can support up to 1,000,000 validators, demonstrating Dill’s scalability to accommodate and secure a large number of participants. A high number of validators helps increase the degree of distribution and decentralization, as well as enhances the security of the network.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Dill uses a PoS model and shares security from large networks like BTC and ETH. This allows existing BTC and ETH users to participate in Dill without additional costs, increasing Dill’s accessibility and appeal to the existing user community.
Roadmap
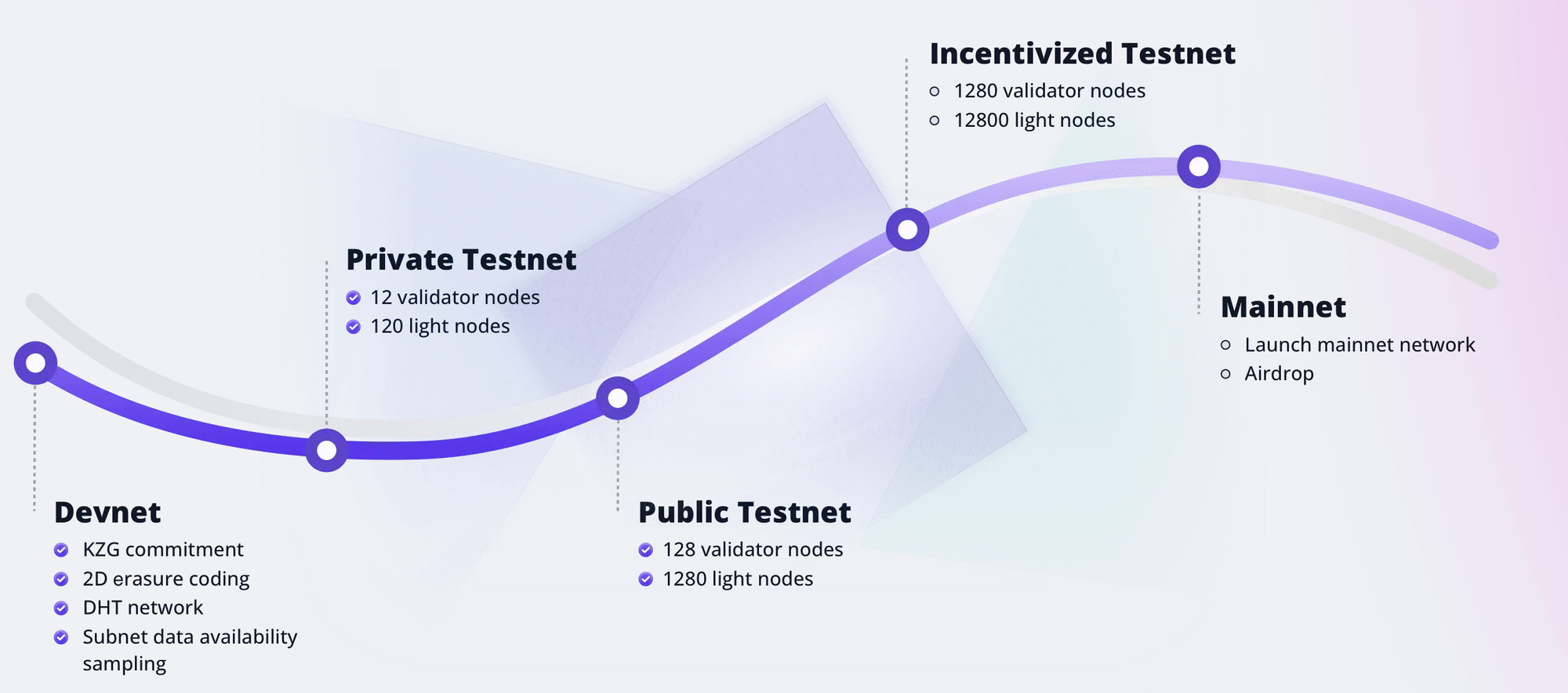
Currently, Dill is still in the testnet phase, with the mainnet expected to launch in Q4 2024 or Q1 2025.
Backer and Investors

Backer:
- FSL (Find Satoshi Lab): A well-known Web3 development studio with products like STEPN, DOOAR, and MOOAR. FSL specializes in bridging Web2 users to Web3.
- Modular Capital: An investment fund focused on blockchain and decentralized technology projects.
- LayerZero: A blockchain infrastructure platform that connects different blockchains, with angel investors from LayerZero.
Individual Investors:
- Santiago R Santos: A well-known angel investor in the blockchain and crypto space.
- TN (Co-founder of Pendle): Contributing from the DeFi sector through the Pendle protocol.
- Victor (Co-founder of Manta): Focused on security and privacy in blockchain.
- Saku (Co-founder of Matr1x): Associated with another project in the blockchain field.
In summary, Dill is supported by reputable organizations and individuals, enhancing the project's potential for growth in the blockchain space.
Dill is a promising project with a strong technological foundation, supported by reputable investment funds and individuals in the industry. Dill’s focus on scalability, security, and decentralization indicates that it has the potential to become a standout project in the blockchain space in the future. However, like any other blockchain project, Dill's success will depend on its execution and community adoption in the coming time.
Top post

Blockcast: Accelerating the Internet, Connecting the World
What is Blockcast? Blockcast is a next-generation Content Delivery Network (CDN) that uses multicast technology to address bandwidth challenges in the era of booming streaming. Born at UC Berkeley, the project aims to build a decentralized network that leverages community power to deliver high-quality content like 4K and 8K globally while slashing costs for providers. With the slogan "Content Delivery, Powered By You!", Blockcast is not just a technology but an ecosystem where anyone can parti
June 2, 2025

Analysis of Nockchain: A ZK-Proof-of-Work Blockchain
Introduction to Nockchain In the fast-evolving world of blockchain, Nockchain emerges as a unique project aiming to revolutionize decentralized computing. Founded in 2023 in Berlin, Germany, Nockchain is a high-throughput blockchain leveraging a Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machine (ZKVM) and a novel ZK-Proof-of-Work (ZKPoW) consensus mechanism. With its native token, $NOCK, and a promise of a fair launch, Nockchain has sparked interest in the Web3 community. However, controversies at its mainnet lau
May 29, 2025

Monad: The Future of Layer 1 Blockchain with Unparalleled Performance
As the blockchain industry continues to evolve, Monad emerges as a promising Layer 1 (L1) blockchain, delivering exceptional performance and scalability. Aiming for 10,000 transactions per second (TPS), a block time of just 0.5 seconds, and full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), Monad is capturing the attention of developers and users alike. Let’s dive into the details of this groundbreaking project and discover how you can get involved today! What is Monad? Monad is a La
May 12, 2025

Drosera Network: Revolutionizing DeFi Security and How to Run a Node
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has transformed the financial landscape, but with great innovation comes great risk. Since 2014, DeFi protocols have lost nearly $80 billion to exploits, highlighting the urgent need for robust security solutions. Enter Drosera Network, a decentralized security protocol built on Ethereum that aims to safeguard DeFi ecosystems through automated threat detection and response. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what Drosera Network is, why it matters, and provide a s
April 20, 2025

Gensyn: Revolutionizing AI Compute and Guide to Running a Node
Introduction to the Gensyn Project Gensyn is a decentralized Machine Learning Compute Protocol designed to connect global computing resources into a supercluster tailored for artificial intelligence (AI). Developed by a UK-based team, Gensyn aims to reduce the costs of training AI models, increase accessibility for researchers, engineers, and academics, and ensure transparency and censorship resistance through blockchain technology. Goals and Vision * Cost Reduction: Gensyn claims it can cu
April 14, 2025

Pipe Network: The Future of Decentralized CDN and Opportunities from the Node DevNet 2 Program
In the digital era, where the speed of content delivery is a critical factor, content delivery networks (CDNs) have become indispensable in ensuring a seamless user experience. However, giants like Cloudflare and Akamai, while powerful, remain constrained by their traditional centralized models. Enter Pipe Network—a decentralized CDN built on the Solana blockchain—emerging as a fresh contender promising to revolutionize how we approach content distribution. Notably, its current Node DevNet 2 pro
March 18, 2025